Higher MCH is a term that often surfaces in discussions about health and wellness, particularly in relation to nutrition and blood health. This article aims to delve deep into the concept of higher MCH, its significance, causes, and implications for health. By the end of this article, readers will have a thorough understanding of what higher MCH is and how it affects overall well-being.
As we explore the intricacies of higher MCH, it is essential to recognize its role in the body. MCH, or Mean Corpuscular Hemoglobin, is a crucial parameter that indicates the average amount of hemoglobin present in red blood cells. Elevated levels of MCH can indicate various health conditions, making it vital for individuals to be informed about what this means for their health.
This article is structured to provide a clear understanding of higher MCH, discussing its definition, causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options. The information provided will be backed by reputable sources to ensure reliability and accuracy, adhering to the principles of Expertise, Authoritativeness, and Trustworthiness (E-E-A-T).
Table of Contents
- What is Higher MCH?
- Importance of MCH in Health
- Causes of Higher MCH
- Symptoms of Higher MCH
- Diagnosis of Higher MCH
- Treatment Options for Higher MCH
- Preventive Measures and Lifestyle Changes
- Conclusion
What is Higher MCH?
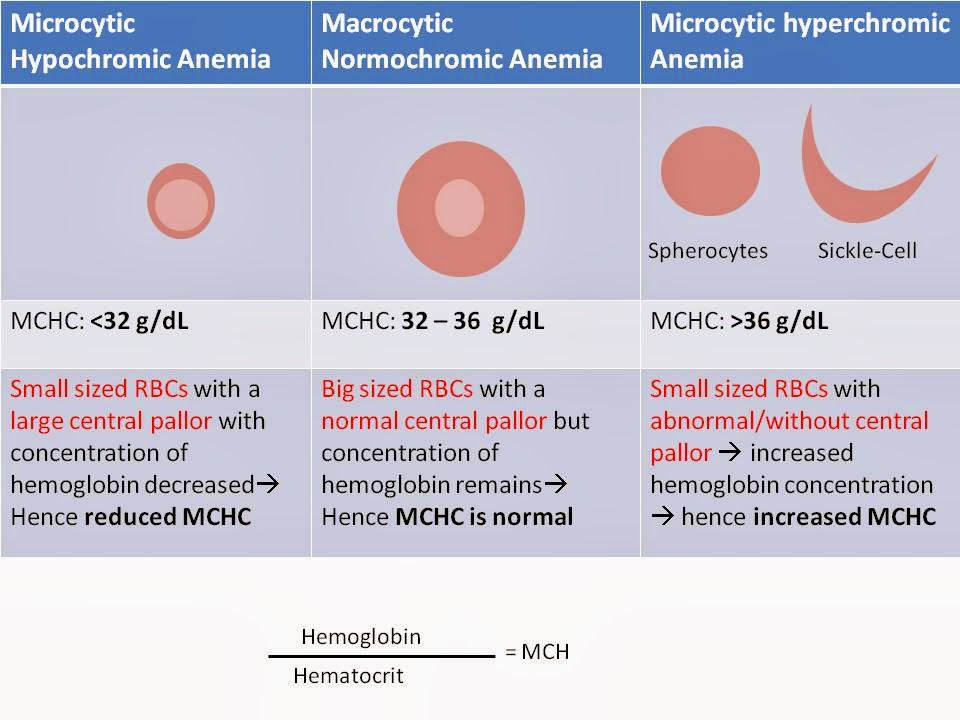
Higher MCH refers to an increased level of Mean Corpuscular Hemoglobin, which is a measurement of the average amount of hemoglobin within each red blood cell. Hemoglobin is essential for transporting oxygen throughout the body, and variations in MCH can indicate various health issues.
Understanding MCH Values
The normal range for MCH typically falls between 27 to 31 picograms per cell. Values exceeding this range may indicate higher MCH, suggesting that the red blood cells contain more hemoglobin than average. This condition can lead to several health implications that warrant attention.
Importance of MCH in Health
Understanding MCH is crucial for overall health assessment. It provides insights into the oxygen-carrying capacity of the blood and helps in diagnosing various conditions related to anemia and other blood disorders.
MCH and Oxygen Transport
A higher MCH can signify that the body is producing larger red blood cells, which may be a compensatory mechanism in response to lower oxygen levels or other factors. Monitoring MCH is essential for evaluating how effectively the blood can deliver oxygen to tissues and organs.
Causes of Higher MCH
Several factors can contribute to elevated MCH levels, including:
- Vitamin B12 Deficiency
- Folic Acid Deficiency
- Liver Disease
- Hypothyroidism
- Alcoholism
Vitamin Deficiencies
Vitamin B12 and folic acid are crucial for the production of healthy red blood cells. Deficiencies in these vitamins can lead to the production of larger cells, thereby increasing MCH levels.
Symptoms of Higher MCH
While higher MCH itself may not produce symptoms, underlying conditions that lead to elevated MCH can manifest through various signs, including:
- Fatigue
- Pale or jaundiced skin
- Shortness of breath
- Heart palpitations
Recognizing Underlying Conditions
It is crucial to address any symptoms that may arise, as they could indicate more severe health issues related to elevated MCH levels.
Diagnosis of Higher MCH
Diagnosing higher MCH typically involves a complete blood count (CBC) test, which provides a comprehensive overview of various blood parameters, including MCH.
Interpreting Blood Test Results
When reviewing MCH levels, healthcare providers consider other related parameters such as Mean Corpuscular Volume (MCV) and Mean Corpuscular Hemoglobin Concentration (MCHC) to obtain a complete picture of an individual’s hematological health.
Treatment Options for Higher MCH
Treatment for higher MCH generally focuses on addressing the underlying causes. Some common treatment approaches include:
- Vitamin supplementation for deficiencies
- Managing underlying health conditions (e.g., liver disease)
- Dietary changes to improve nutrition
Consultation with Healthcare Providers
It is essential for individuals with higher MCH levels to consult with healthcare professionals for personalized treatment plans and monitoring.
Preventive Measures and Lifestyle Changes
Preventing higher MCH levels involves adopting a healthy lifestyle, including:
- Eating a balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals
- Avoiding excessive alcohol consumption
- Regular health check-ups to monitor blood health
Importance of Regular Screening
Regular blood screenings can help detect potential issues early, allowing for timely interventions that can prevent complications associated with higher MCH.
Conclusion
Higher MCH is a significant health parameter that can indicate underlying health issues. Understanding its implications, causes, and treatment options is vital for maintaining optimal health. If you suspect that your MCH levels may be elevated, it is essential to consult with a healthcare provider for proper evaluation and management.
We encourage readers to leave comments, share their experiences, or ask questions about higher MCH. Additionally, feel free to explore other articles on our site for more information on health and wellness.
Thank you for reading, and we hope to see you back here for more informative content!